Court Records
Research Guides
About the Records
The most frequently requested court records at the Utah State Archives are divorce decrees, naturalization or citizenship records, documentation of name changes, probate records, and criminal cases.
District Courts, 1896-present
The district court is the state trial court of general jurisdiction. The district court has original jurisdiction for all civil cases and all criminal felonies: homicides, assaults, sex and drug offenses, forgery, arson, robbery, and misdemeanors in certain circumstances.
An important part of the district court caseload is domestic relations cases, such as divorces, child custody and support, adoption, and probate. District judges have the power to issue extraordinary writs. Also, naturalization was often handled by the courts.
Beginning in 1896, the records for each county were kept separately. There are now eight judicial districts, consult the historical jurisdictional chart to know the districts that counties fell under in the past.
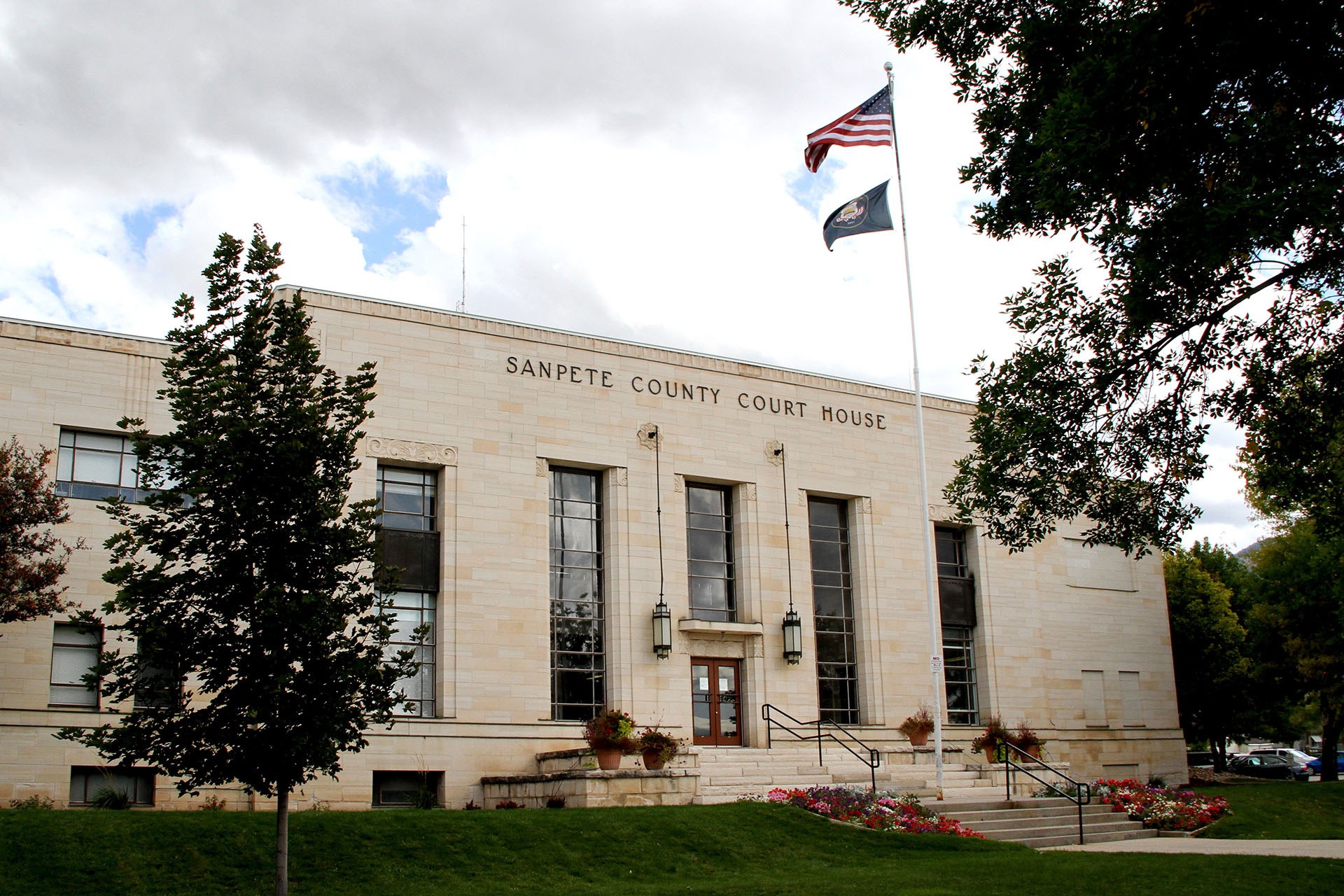

- Box Elder County
- Cache County
- Rich County
- Davis County
- Morgan County
- Weber County
- Salt Lake County
- Summit County
- Tooele County
- Juab County
- Millard County
- Utah County
- Wasatch County
- Beaver County
- Iron County
- Washington County
- Garfield County
- Kane County
- Piute County
- Sanpete County
- Sevier County
- Wayne County
- Carbon County
- Emery County
- Grand County
- San Juan County
- Daggett County
- Duchesne County
- Uintah County
Territorial Courts, 1850-1895
The legislature of the proposed State of Deseret approved on January 9, 1850 county courts and justices of the peace. County Probate Courts were established by the legislature in January 1851. They could also hear appeals from justice of the peace courts.

Court Case and Document Types
Document Types
- Minute books
- A daily chronological record of court proceedings and often include lists of jury members, names of attorneys admitted to practice, information about financial accounts and the collection of fees, and sometimes the text of orders of the court.
- Register of actions (or docket book)
- Provides a summary of proceedings in each case including a brief abstract of motions and orders, the amount of fees collected, and the eventual disposition.
- Order or judgment books
- Record the text of each document and the amount of any monetary judgment.
- Probate Record Books
- The text of documents and orders filed in probate matters are copied into probate record books.
- Case Files
- The bulk of a court's records consists of case files arranged numerically by the case number assigned at the time the petition or complaint initiating the case was filed. Case files generally include the original papers filed by attorneys or issued by the court such as petitions, motions, indictments, complaints, subpoenas, depositions, affidavits, writs, and judgments or decrees.
- Transcripts*
- An official and certified copy of what transpired in court or at an out-of-court deposition
- Exhibits*
- Documentation or items of real evidence
*Both have a short retention period. These records typically are not transferred to the state archives, however in rare cases they were included in the case file.

Court Cases
The main types in all eras are civil, criminal, and probate. Within those types are records that are commonly researched on their own, such as divorce proceedings being a civil case record. Case files and other documents are retained by the court until about fifty years have passed, when they may be transferred to us.
- Civil cases are private lawsuits concerning a failed legal responsibility such a breach of contract, negligence, divorce, and copyright.
- Criminal cases are when the government charges a defendant for a crime and are retained long term generally only for felony crimes. These records may be subject to expungement procedures.
- Probate cases most often establish a valid will for the estate of a deceased person, but also concern adoptions and legal name changes.
Historical Jurisdictions
To search for court records, you’ll need the jurisdiction for the case. Most often, this will be the county of residence (or location for a business) of one or both parties. This chart compiles historical jurisdiction information for all counties, including those now extinct, in Utah from the territorial period to the present.
(N) = Northern Division of First District
(S) = Southern Division of First District
Extinct Counties in Territorial Court Districts
Page Last Updated March 27, 2024.
About this Guide
Written by Glen Fairclough (document types) and originally published in June 1999.
You might also like...
Utah State Courts
Contact information, help, and other resources for the judicial branch.
Historical Boundaries Exhibit
Discover the history of county, court, and other boundaries in Utah.
Civil Court Records
Research civil lawsuits including divorce, contracts, and copyright.
Criminal Court Records
Research records of criminal felonies and similar actions.